Understanding Sei: A Comprehensive Overview
Apr 11, 2024 ⋅ 18 min read
Key Insights
- Sei has positioned itself as a fast and efficient Layer-1 network that is compatible with CosmWasm and Cosmos' IBC protocol.
- Its "Twin-Turbo Consensus" mechanism reduces transaction latency through intelligent block propagation and optimistic block processing, enhancing the speed of transaction execution and network consensus.
- Parallel execution increases transaction throughput, as transactions are executed in parallel independent of each other.
- The upcoming Sei V2 upgrade will introduce several technological upgrades — namely, full backward compatibility for EVM smart contracts and tokens, optimistic transaction parallelization, and a re-architecture of the network’s storage interface.
- Based on the 7-day moving average on April 9, 2024, Sei averages 8,300 daily active addresses and 394,000 daily transactions. It also has a DeFi TVL of $38.7 million.
Introduction
The heightened activity in the prior bull market exposed some limitations in blockchain technology as networks experienced high gas fees and slow transaction speeds. However, in the recent bear market, new Layer-1 networks emerged with technological innovations that hoped to address these limitations. Sei was no exception, as Sei Labs created a Layer-1 network with the goal of becoming the fastest network for exchanging digital assets. Sei’s built-in blockchain technologies, such as Twin-Turbo Consensus and transaction parallelization, enable reduced transaction latency and increased transaction throughput. Sei competes with other alternative Layer-1s such as nascent, non-EVM Layer-1 networks like Sui and Aptos, incumbents like Solana, and the upcoming parallelized EVM in Monad. As the network continues to mature, the technological upgrades planned with Sei V2 and later with the Parallel Stack will further differentiate Sei and catalyze growth.
Background
Sei was announced in May 2022 and founded by Jayendra Jog and Jeff Feng. Both founders offer unique prior experience, including those gained by serving as a software engineer at Robinhood and venture investor at Coatue Management. Following Sei’s announcement, Sei Labs raised $35 million across two rounds and conducted two incentivized testnets.The Seinami Incentivized Testnet, also known as Atlantic-1, went live in July 2022. In March 2023, an upgraded Atlantic-2 testnet went live. Finally, in August 2023, Sei launched its Pacific-1 mainnet alongside SEI, its native token that was airdropped to eligible users. Since the mainnet launch, network activity has grown, and the onchain ecosystem has expanded with the help of Sei Foundation. Sei Labs is working toward major technological upgrades in the Public Devnet for the upcoming launch of Sei V2 in H1 2024.
Technology
Sei is an integrated, general-purpose Layer-1 network. As an integrated blockchain, Sei combines the responsibilities of execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability into a single network. The blockchain is compatible with Cosmos’ Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol and was built through modified forks of the Cosmos SDK and Tendermint Core protocol. Sei’s application layer supports CosmWasm smart contracts written in Rust. Despite being built with Cosmos technologies, Sei is sovereign in both architecture and governance.
The network’s built-in features enhance transaction efficiency and throughput, supporting Sei’s goal of becoming the fastest network for exchanging digital assets. These features include Twin-Turbo Consensus, which serves to reduce transaction latency, and transaction parallelization, which serves to increase transaction throughput. Additionally, an onchain central limit order book (CLOB) supports liquidity across the network, though it’s set to be deprecated. Sei’s initial set of technological features will be expanded upon in the upcoming Sei V2 upgrade.
Note: This Technology section focuses primarily on Sei’s current technology. For a more in-depth look at technological upgrades planned for the upcoming launch of Sei V2, please see the Roadmap section of this report.
Consensus
Sei relies on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) protocol based on Tendermint Core, a Byzantine fault-tolerant (BFT) algorithm used to achieve consensus. Sei validators process transactions and settle state (account balances, smart contracts, etc.) changes on the network. Validators are selected to produce blocks according to their total stake (self-bonded plus delegated SEI tokens). Anyone that meets the hardware requirements can operate a validator node to secure the network. Today, only the top 39 validators by total stake are able to participate in consensus and earn network transaction fees and staking rewards. An active validator's total stake can be slashed and burned if they misbehave. SEI tokenholders can delegate SEI to an existing validator, enabling delegators to help secure the network. The delegators also share in the associated validator’s SEI rewards, minus the associated validator’s chosen commission rate. Both validators and delegators must wait a 21-day unbonding period before fully unbonding SEI that has been staked. Notably, non-vested tokens can be staked to secure the network.
Sei also leverages its novel “Twin-Turbo Consensus” mechanism that serves to reduce transaction latency through two main components:
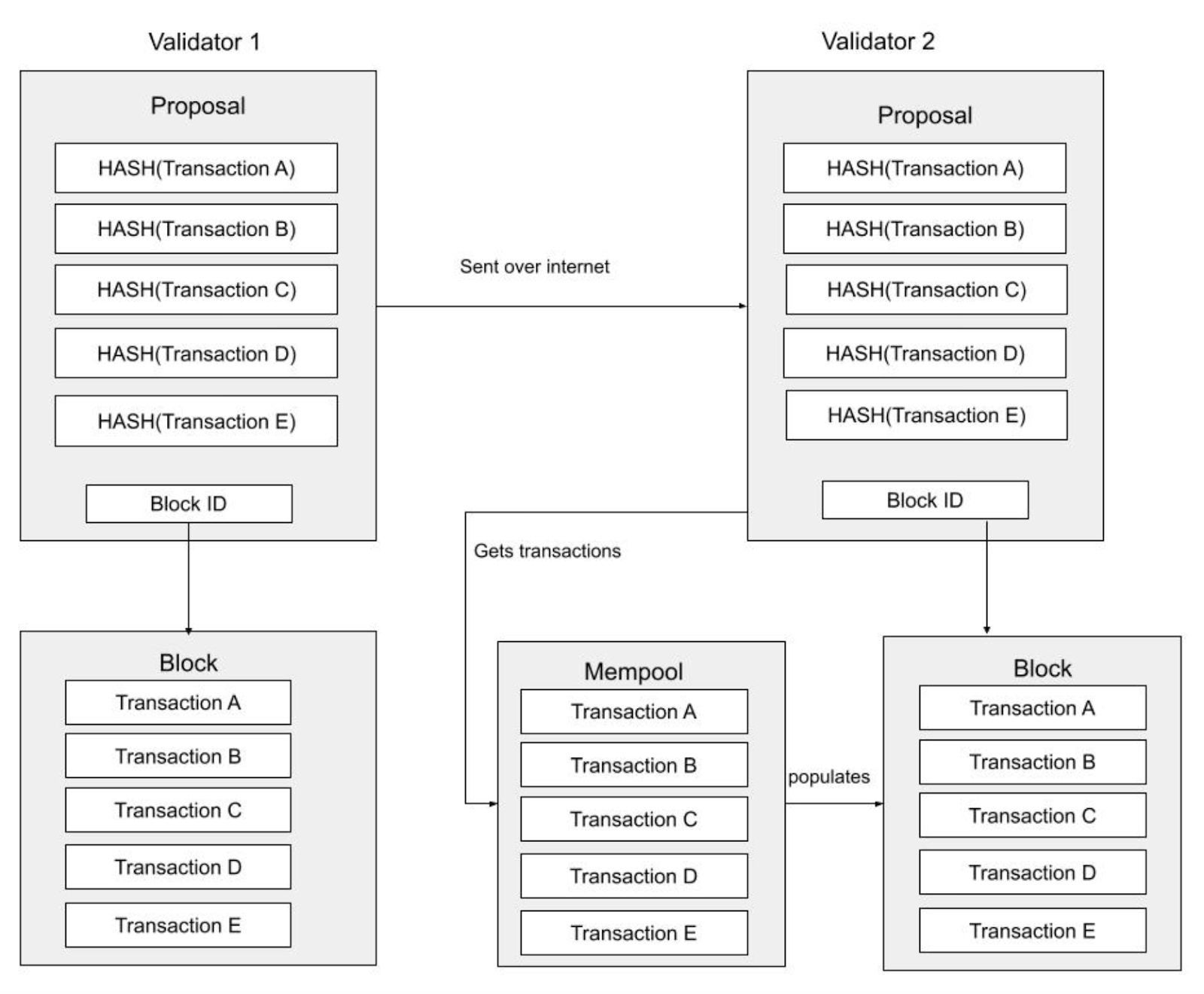
Source: Sei Blog
Intelligent Block Propagation: A block proposer creates a block of transactions that is distributed across the validator set. These blocks are compressed to include hashes of each transaction included in the block. Normally, validators would need to wait for the entire contents of the proposed block to arrive before proceeding with consensus. However, Sei’s design allows individual transactions in a proposed block to be received while validators take advantage of the individual transactions already in their mempools.If all the necessary transactions are held in a mempool, a validator can reconstruct a proposed block locally without waiting to receive the entire contents of the proposed block. This decreases the amount of time validators must wait to reconstruct proposed blocks, decreasing transaction latency.
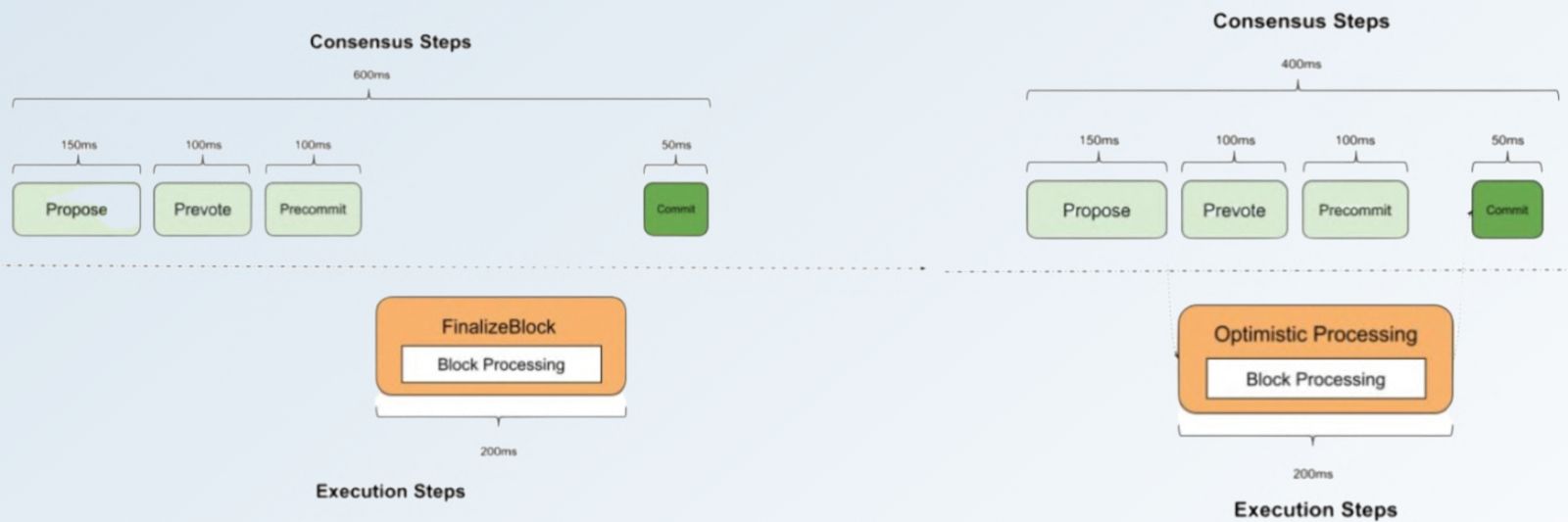
Source: Sei Blog
Optimistic Block Processing: Normally, validators perform the prevote and precommit steps before coming to consensus on a proposed block and committing it to the blockchain. However, on Sei, the contents of a proposed block are optimistically assumed to be valid once they have been reconstructed by a validator. This processing occurs simultaneous to the prevote and precommit steps. Validators immediately begin to process the first block proposal they receive, even before the blocks are confirmed by consensus. This process helps decrease transaction latency. If the validator set were to fail to reach consensus on the optimistically accepted contents of a proposed block, the network would reject the block, and future rounds for that block height would not use optimistic block processing.Notably, Intelligent Block Propagation and Optimistic Block Processing come with the tradeoff of Quadratic Communication Complexity. In other words, the number of messages sent between the validator set increases exponentially, making it difficult to increase the maximum validator set size due to increased bandwidth and processing requirements.
Execution
Many blockchains have a sequential transaction engine, where transactions are ordered and executed one by one. To speed up execution, transactions on Sei can be executed in parallel, allowing smart contracts to operate without interference from each other. This results in reduced network congestion and increased transaction throughput. Today, parallelization on Sei is optional and pessimistic. To take advantage of Sei’s parallelization capabilities, smart contract developers must define the state (account balances, smart contracts, etc.) that smart contracts use. If not defined, transactions are processed sequentially. If defined, “dependency mappings” are maintained for the network to know (1) which transactions can be run in parallel, independent of one another, and (2) which transactions cannot be run in parallel because they depend on each other. These dependency mappings are created through Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG). If dependencies between transactions are found to exist (i.e., they read/write the same location within Sei’s state), they are processed sequentially, making execution on Sei “hybridized.”
Roadmap
In November 2023, Sei announced its plans for Sei V2, which will introduce three major upgrades to the network. In February 2024, Sei launched its Public Devnet to test Sei V2 functionality. The upgrade is expected to be deployed to mainnet sometime in H1 2024. Lastly, once Sei V2 goes live, the team plans to launch Sei’s Parallel Stack, which would enable Layer-2 networks rolling up to Sei.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) Integration

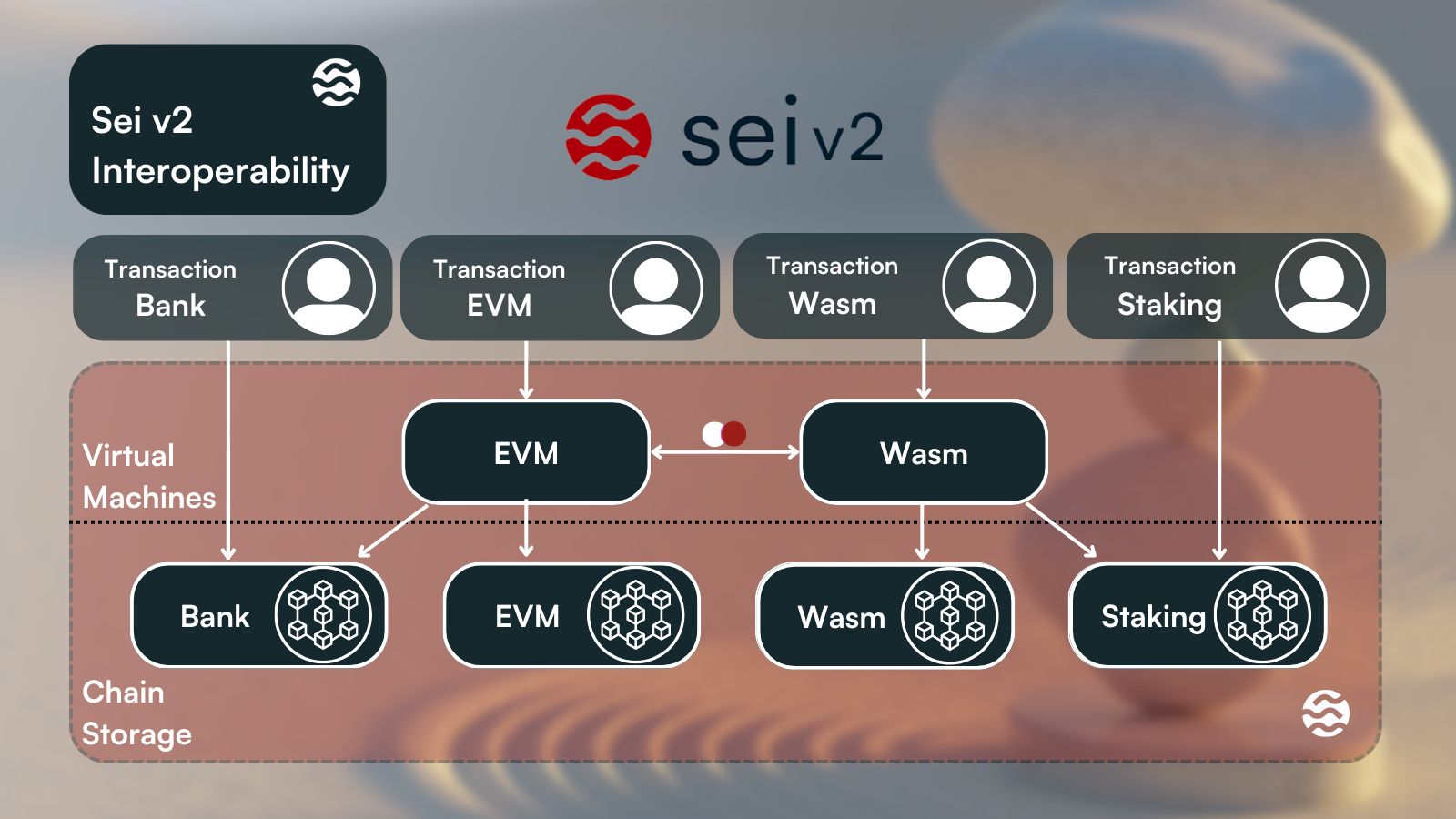
Source: Sei Blog
Sei V2 plans to introduce compatibility for EVM smart contracts written in Solidity, including the ERC-20 and ERC-721 token standards. EVM smart contracts will also be backward compatible, meaning that smart contracts on Ethereum and its Layer-2 networks can be seamlessly redeployed on Sei.
Source: Sei Blog
In effect, Sei will simultaneously support two execution environments. Also, each user’s EVM and Wasm addresses will be linked and will share the same underlying account. EVM smart contracts and tokens will be interoperable with existing CosmWasm smart contracts, and vice versa, through the use of Pointer Contracts and Precompiled Contracts.
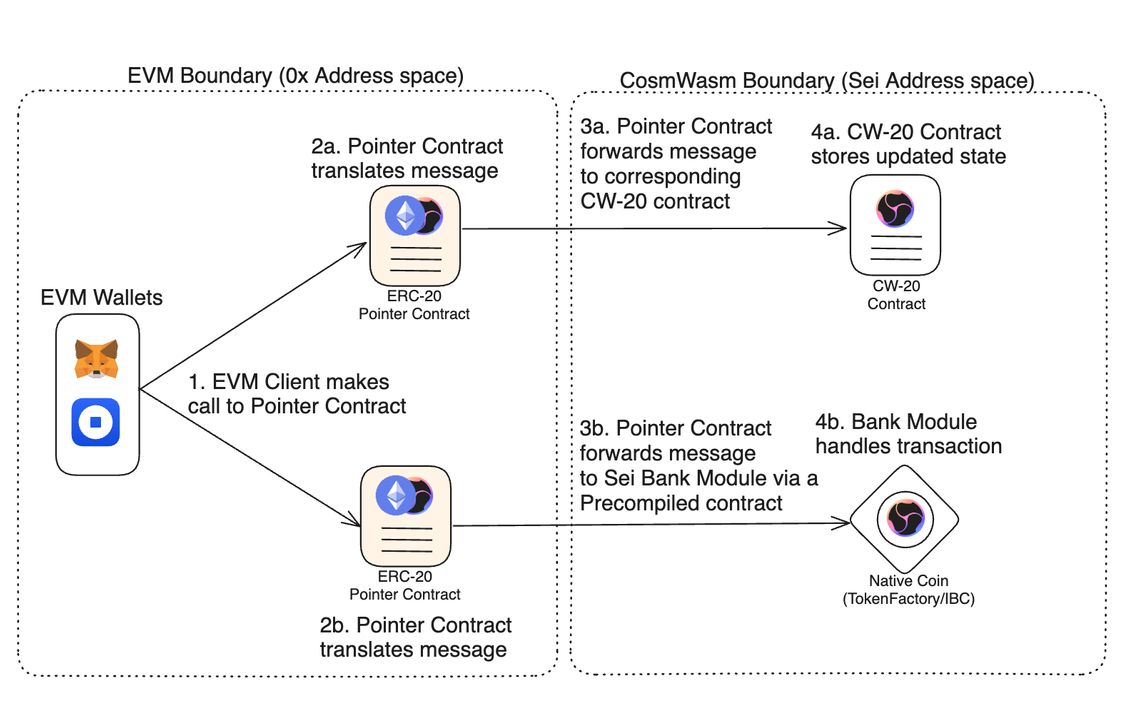
Source: Sei GitBook
These contracts will make tokens accessible in both environments without needing a wrapped version of the token. In essence, Pointer Contracts act as a “translator” between the two execution environments. They allow users to signal what messages they want to send across either environment. With the introduction of EVM compatibility, Sei would become a suitable destination for cross-chain EVM protocols to be deployed on. Many of the leading protocols on Ethereum also exist on other EVM-compatible networks. This upgrade could lead to EVM infrastructure and DeFi protocols being deployed on Sei, bootstrapping a robust EVM ecosystem on the network. The upgrade will also allow EVM developers to be able to build on the network. Per Electric Capital’s 2023 Developer Report, 87% of multichain developers work on at least one EVM chain. This previously inaccessible developer ecosystem will be able to take advantage of Sei’s enhanced transaction efficiency and throughput to create novel EVM applications that are native to Sei. Evidence of this can already be seen through the EVM applications being built on Sei’s Public Devnet.
Optimistic Parallelization
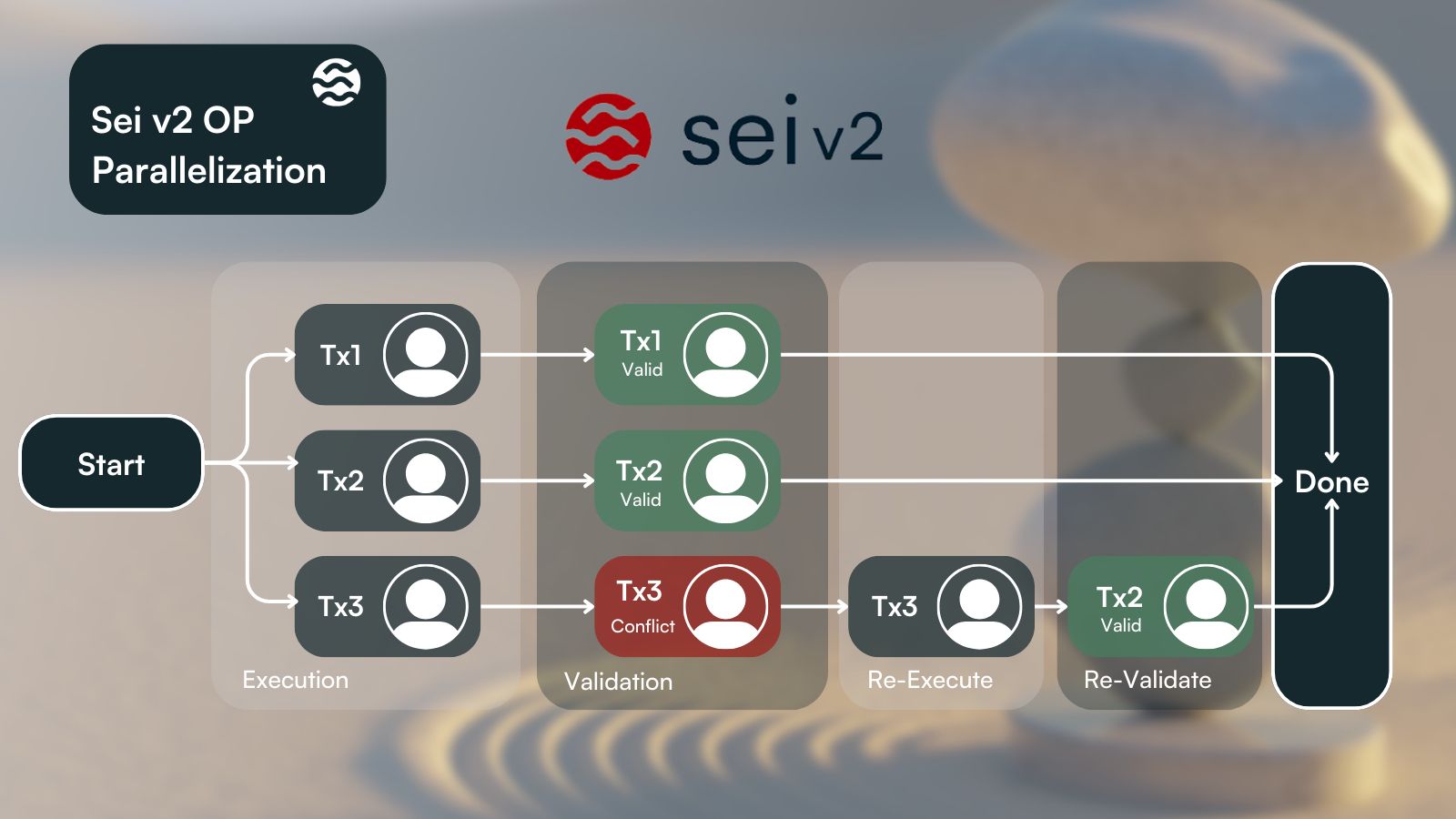
Source: Sei Blog
Parallelization on Sei is currently optional. To take advantage of Sei’s parallelization capabilities, smart contract developers must define the state (account balances, smart contracts, etc.) that smart contracts use. Sei V2 plans to change from pessimistic parallelization by introducing optimistic parallelization, where all transactions will optimistically be assumed to be eligible for parallel processing. Similar to Sei’s optimistic block processing fallback, if dependencies between transactions exist (transactions interacting with the same part of Sei’s state), they will be re-processed sequentially. The change to optimistic parallelization will ease the developer experience by not requiring dependency mappings to be defined.
SeiDB

Source: Sei Blog
Sei V2 plans to re-architecture the network’s storage interface. SeiDB would introduce a new storage layer on Sei that decouples the State Commitment (SC) Layer and State Store (SS) Layer. This is expected to:
- Improve state read/write performance leading to increased state sync times and decreased commit times for faster time to finality.
- Decrease state bloat with less metadata needing to be stored.
- Reduce hardware requirements for node operators.
Parallel Stack
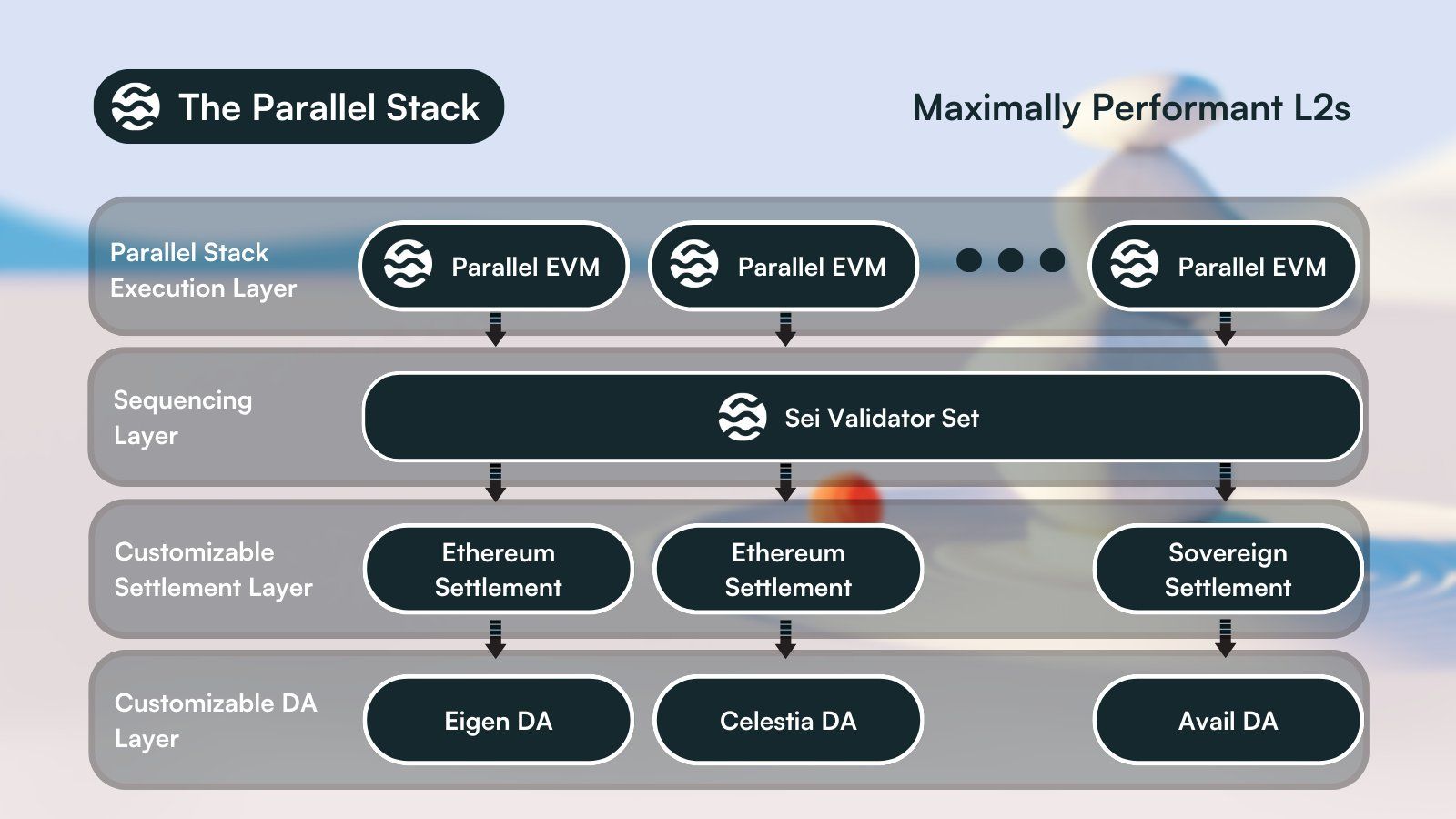
Source: Sei Blog
Modular blockchains separate one or more of the responsibilities of execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability (DA). Modular blockchains emerged throughout 2022 with launches of Ethereum Layer-2s that specialized as execution layers. In 2023, networks specialized as DA layers began to launch. Sei plans to join the modular blockchain arena once Sei V2 is live and Sei is EVM-compatible. Specifically, Sei’s upcoming open-source Parallel Stack is planned to enable developers to launch modular, Layer-2 blockchains that serve as parallel EVM execution layers. These Layer-2s could use Sei’s validator set for sequencing services and customize their settlement and DA layers.
Note: Per a third-party Binance report, future planned upgrades for H1 2024 also include (i) “MEV Auctions,” (ii) “Intra-Validator Sharding,” and (iii) “ZK Light Clients.” However, the project team has not disclosed further details on these plans. Thus, they have not been covered in this report.
SEI Token
SEI is the native token of Sei that was launched upon the network’s Pacific-1 mainnet launch on Aug. 16, 2023. SEI currently has a maximum token supply of 10 billion. As of April 9, 2024, SEI’s total token supply is ~8.70 billion, of which ~65.18% is staked (~5.67 billion), and ~31.72% is circulating (~2.76 billion). The remaining ~1.30 billion SEI are scheduled to be minted over 10 years as inflationary token rewards distributed to Sei’s active validator set. The SEI token serves several functions for Sei, including (1) settling network transaction fees, (2) being staked by validators and delegators, (3) rewarding validators, and (4) participating in governance.
Tokenomics
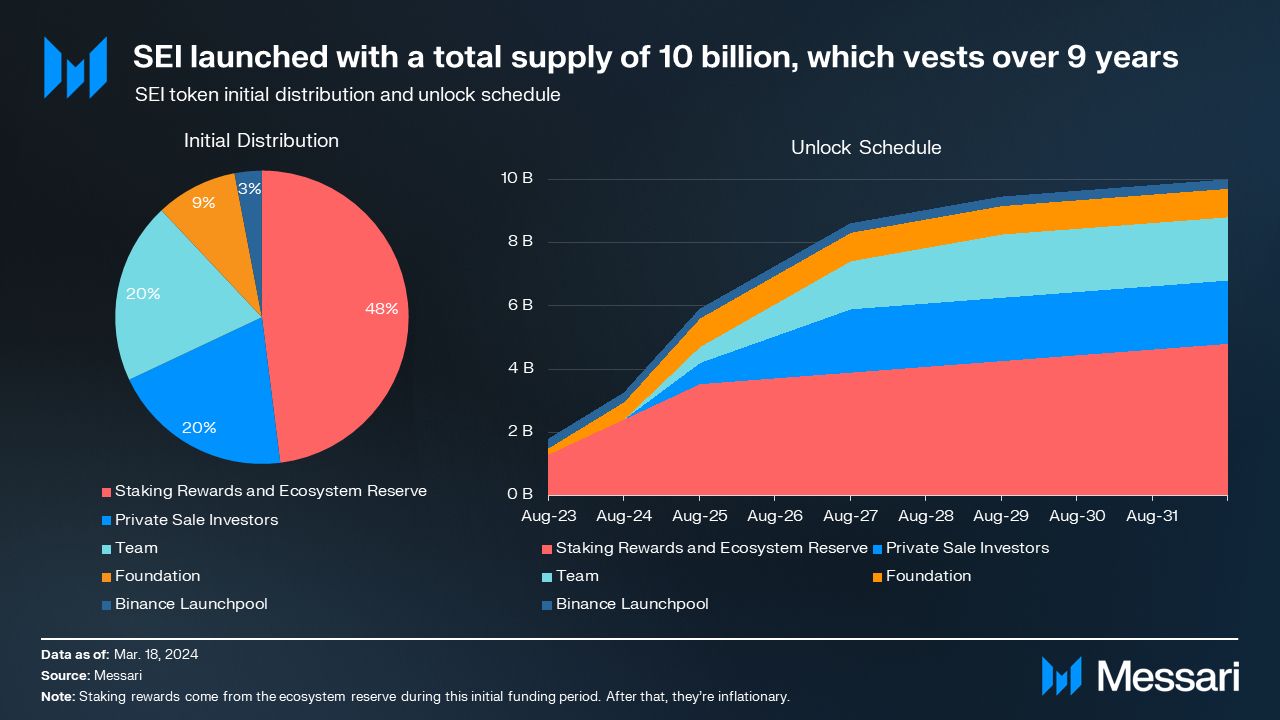
SEI tokens were allocated across five areas:
- Ecosystem Reserve (48% of the total supply): 4.80 billion tokens were allocated to an “Ecosystem Reserve” controlled by Sei Foundation. This reserve is meant to fund staking rewards, ecosystem initiatives, airdrops, and incentives. Of this allocation, 27% was available upon the token genesis, while the remaining 73% is subject to nine years of variable vesting.
- 300 million SEI (3% of the total supply) were allocated to an airdrop from the Ecosystem Reserve allocation. Eligible users included those that participated in Sei’s incentivized Atlantic testnet. The project team did not specify eligibility criteria, though official task campaigns during the testnet included the “Dawn NFT,” “Dusk NFT,” and “Sunken Treasure NFT.” Sei also conducted campaigns via Galxe. Additionally, “active users” of Solana, Ethereum, Arbitrum, Polygon, Binance Smart Chain, and Osmosis that bridged assets to Sei were eligible.
- 1.50 billion SEI (15% of the total supply) were allocated to be minted over 10 years as inflationary token rewards distributed to Sei’s active validators.
- Sei Foundation has not communicated how much of the remaining 3.0 billion SEI (30% of the total supply) is allocated to each Ecosystem Reserve area.
- Private Sale Investors (20% of the total supply): 2.00 billion tokens were allocated to “Private Sale Investors.” The tokens allocated to Private Sale Investors had a one-year cliff followed by three years of linear vesting. Sei Labs has raised $35 million across two rounds.
- In August 2022, $5 million was raised in a seed round led by Multicoin Capital with participation from Coinbase Ventures, Hudson River Trading, and more.
- In April 2023, $30 million was raised in two strategic funding rounds with participation from Jump Crypto, Distributed Global, Flow Traders, and others.
- In November 2023, Circle Ventures completed a strategic investment in Sei.
However, the project team did not disclose whether equity and/or tokens were sold in these rounds.
- Team (20% of the total supply): 2.00 billion tokens were allocated to the “Team,” subject to a one-year cliff followed by five years of variable vesting. Specifically, over the first three years, 76% of tokens are linearly unlocked, while the remaining 24% are linearly unlocked over the final two years.
- Foundation (9% of the total supply): 900 million tokens were allocated to the “Foundation.” Of this allocation, 22% was available upon the token genesis, while the remaining 78% was subject to linear vesting over two years.
- Binance Launchpool (3% of the total supply): 300 million tokens were allocated to a “Launchpool” facilitated through Binance. Users could stake BNB, TUSD, and FDUSD over a 30-day period to earn a proportional share of SEI tokens.
Notably, non-vested tokens such as those allocated to the Team, Foundation, and Private Sale Investors can be staked. These staked tokens earn liquid SEI token rewards and have the ability to participate in governance and secure the network.
Governance
Sei uses an onchain governance process where proposals can affect network parameters. These include parameters related to SEI’s minting schedule or increasing the maximum set of active validators. Sei’s governance does not have an official voting front end, but it can be interacted with through supported wallets such as Fin Wallet and Compass Wallet. The governance process is as follows:
- Create a Proposal: Proposals can be created to initiate a two-day deposit period where SEI can be deposited to support the pending proposal. Once a minimum deposit threshold of 3,500 SEI ($2,400 as of April 9, 2024) is met, the proposal moves to an onchain vote. Expedited proposals are possible by using the “is-expedited” flag, which halves the deposit period to one day but doubles the minimum deposit threshold to 7,000 SEI ($4,800 as of April 9, 2024).
- Deposit Period: SEI can be deposited to support a pending proposal. If the minimum deposit threshold is met, the proposal moves to an onchain vote. If the minimum deposit threshold is not met prior to the deposit period ending, the proposal is canceled, and all deposits are burned.
- Vote on Proposal: Users that stake SEI can vote on an active proposal with one of the following vote types: “yes,” ”no,” “no_with_veto,” or “abstain.” Voting power is equivalent to each user’s respective stake. The voting period is five days, and a quorum of 33% of the staked token supply is required. A simple majority of at least 50% of voting power used on a proposal must vote “yes” to approve the proposal. If over 33% of the total voting power is used to select “no_with_veto,” the proposal will fail regardless of the other votes.
As of April 9, 2024, 48 out of 53 active proposals have passed since Sei’s mainnet launch. These have included several small increases to the maximum set of active validators, increasing governance deposit parameters, updating the minimum network transaction fee, and upgrading network software. Notably, non-vested tokens are able to be staked to participate in governance.
State of the Sei Ecosystem
Since Sei’s mainnet launch in August 2023, protocols across various sectors have launched and grown the network’s ecosystem:
- DeFi: With a total value locked (TVL) of ~$38.7 million on Sei as of April 9, 2024, Sei lags behind competitors Solana (~$4.45 billion in TVL), Sui (~$670.92 million in TVL), and Aptos (~$453.05 million in TVL). Sei’s top decentralized exchange (DEX), Astroport, holds the most with ~$38.3 million in TVL. Perpetual DEXs such as Levana Finance (~$36.6 million in cumulative volume traded) can be used by traders, while lending protocols like Hoyu and Kawa Finance are live on Sei’s Public Devnet.
- Liquid Staking: Protocols like Silo and Kryptonite enable users to liquid-stake SEI tokens through their respective iSEI and stSEI tokens. As of April 9, 2024, Silo and Kryptonite have ~$11.6 million and ~$4.4 million in SEI tokens staked, respectively.
- Wallets: Sei is averaging ~8,300 daily active addresses and ~394,000 daily transactions as of April 9, 2024. The wallet space includes Sei-native wallets in the Fin Wallet and Compass Wallet. SPACE ID offers the .sei Name Service, where over 20,300 NFTs representing human-readable names for Sei addresses have been minted.
- NFTs: The NFT ecosystem on Sei is one of the most active sectors on the network with over $20 million in all-time total volume. Sei-native NFT marketplaces include Pallet Exchange, MRKT, Quik, and Dagora. NFT projects include those such as (1) Seiyans, which is building MRKT, (2) The Colony, which is building AntSwap, and (3) WeBump, which offers a toolkit called Lighthouse that has been used to mint over 500,000 NFTs.
- Gaming: A partnership with Pixel Realm looks to bring their venture fund, gaming marketplace, and gaming studio to Sei.
- DePIN: Nimble Network was launched first on Sei, aiming to decentralize the training of artificial intelligence (AI) models.
Additional officially announced partnerships or integrations include those such as Seijin (a launchpad project), Kado (a crypto on/off-ramp), Tenderly (an EVM developer toolkit), and Space and Time (data indexing). Once Sei’s V2 upgrade goes live and Sei becomes EVM-compatible, various EVM applications are expected to launch, including protocols like Algebra DEX. Additionally, ecosystem growth is also continually spurred through several programs:
- Ecosystem Fund: In September 2022, Sei announced an “Ecosystem and Liquidity Fund” to help early-stage founders and teams acquire users and expand. The Fund launched with $50 million in funding sponsored by Multicoin Capital, Flow Traders, Hudson River Trading, and others. In January 2023, an additional $20 million was secured from MEXC Global. Most recently, in April 2023, another $50 million was secured from Foresight Ventures.
- Creator Fund: In April 2024, Sei announced a creator fund focused on both new and existing NFT and social projects. This fund is in collaboration with Gitcoin, an established leader in community funding for multiple ecosystems.
- Sei Launchpad Program (“sei/acc program”): Managed by Sei Foundation, this program aims to support founders building on Sei through mentorship and investment. Interested parties can apply here.
- Ecosystem Reserve: Sei's Ecosystem Reserve is partially allocated for funding ecosystem initiatives, airdrops, and incentives. No additional ecosystem initiatives, airdrops, or incentives have begun since SEI’s token genesis. However, Sei Foundation continues to have these tokens that could be used to spur future growth of the network and its ecosystem.
Closing Summary
Sei, a Layer-1 blockchain, aims to be the fastest network for exchanging digital assets. It features novel technological features built into its blockchain. Namely, Twin-Turbo Consensus and transaction parallelization, which increase transaction efficiency and throughput. Since launching its mainnet in August 2023, Sei has seen an ecosystem of native projects launch and a community emerge. To maintain momentum, Sei must successfully deploy the features planned for the Sei V2 upgrade. EVM compatibility could unlock new opportunities by expanding Sei’s developer ecosystem and enabling established EVM protocols to deploy on Sei. Optimistic transaction parallelization will ease the developer experience, while SeiDB improves the network’s performance across the board. Post-V2, sights can be set on the Parallel Stack. The stack could enable further growth in Sei’s ecosystem and validator usage as Layer-2 EVM rollups are launched by developers seeking an improved user experience and novel design space. All these planned features could lead to more activity on the network as it continues to mature and differentiate itself from other competing Layer-1 networks.
Let us know what you loved about the report, what may be missing, or share any other feedback by filling out this short form. All responses are subject to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
This report was commissioned by Gladiolus Labs Limited. All content was produced independently by the author(s) and does not necessarily reflect the opinions of Messari, Inc. or the organization that requested the report. The commissioning organization does not influence editorial decision or content. Author(s) may hold cryptocurrencies named in this report. This report is meant for informational purposes only. It is not meant to serve as investment advice. You should conduct your own research, and consult an independent financial, tax, or legal advisor before making any investment decisions. Past performance of any asset is not indicative of future results. Please see our Terms of Service for more information.
No part of this report may be (a) copied, photocopied, duplicated in any form by any means or (b) redistributed without the prior written consent of Messari®.
Upgrade to Messari Pro
Gain an edge over the market with professional grade tools, data and research.
Already a member? Sign in
Upgrade to Messari Pro
Gain an edge over the market with professional grade tools, data and research.
Already a member? Sign in
Patryk is an Experienced Research Analyst at Messari whose areas of expertise include Layer-1 and Layer-2 networks, infrastructure, and stablecoins. Previously, Patryk worked as a Financial Crimes Consultant and studied finance at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Read more
Research Reports
Read more
Research Reports
About the author
Patryk is an Experienced Research Analyst at Messari whose areas of expertise include Layer-1 and Layer-2 networks, infrastructure, and stablecoins. Previously, Patryk worked as a Financial Crimes Consultant and studied finance at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.